How to Count Lines of Code in Bitbucket to Decide what SonarQube License You Need
SonarQube is a popular automatic code review tool used to detect bugs and vulnerabilities in the source code through static analysis. While the Community Edition is free and open-source, the Developer, Enterprise, and Data Center editions are priced per instance per year and based on the number of lines of code (LOC). So if you are considering buying a license for SonarQube, you need to count lines of code in Bitbucket for all projects and repositories you want to analyze.
In this post, we’ll show how you can count LOC for your Bitbucket Data Center instance, as well as for each project or repository using the Awesome Graphs’ REST API resources and Python.
Awesome Graphs for Bitbucket is a data-providing and reporting tool that allows you to export commits, lines of code, and pull requests statistics on global, project, repository, and user levels. It also offers out-of-the-box graphs and reports to deliver instant answers to your questions.
How to count lines of code for the whole Bitbucket instance
Getting lines of code statistics for the whole Bitbucket instance is pretty straightforward and will only require making one call to the Awesome Graphs’ REST API. Here is an example of the curl command:
curl -X GET -u username:password "https://bitbucket.your-company-name.com/rest/awesome-graphs-api/latest/commits/statistics"
And the response will look like this:
{
"linesOfCode":{
"added":5958278,
"deleted":2970874
},
"commits":61387
}
It returns the number of lines added and deleted as well as the total number of commits in all Bitbucket projects and repositories. To get the total LOC, you’ll simply need to subtract the number of deleted from the added.
Please note that blank lines are also counted in lines of code statistics in this and the following cases.
How to count lines of code for each project in the instance
You can also use the REST API resource to get the LOC for a particular project, but doing this for each project in your Bitbucket instance will definitely take a while. That’s why we are going to automate this process with a simple Python script that will run through all of your projects, count the total LOC for each one, and then will save the list of project keys with their total LOC to a CSV file.
The resulting CSV will look like this:
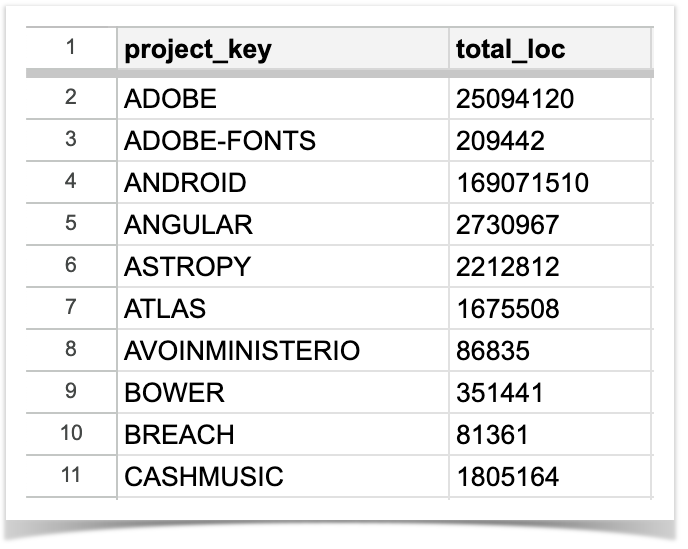
Here is the script to get it:
import requests
import csv
import sys
bitbucket_url = sys.argv[1]
bb_api_url = bitbucket_url + '/rest/api/latest'
ag_api_url = bitbucket_url + '/rest/awesome-graphs-api/latest'
s = requests.Session()
s.auth = (sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3])
def get_project_keys():
projects = list()
is_last_page = False
while not is_last_page:
request_url = bb_api_url + '/projects'
response = s.get(request_url, params={'start': len(projects), 'limit': 25}).json()
for project in response['values']:
projects.append(project['key'])
is_last_page = response['isLastPage']
return projects
def get_total_loc(project_key):
url = ag_api_url + '/projects/' + project_key + '/commits/statistics'
response = s.get(url).json()
total_loc = response['linesOfCode']['added'] - response['linesOfCode']['deleted']
return total_loc
with open('total_loc_per_project.csv', mode='a', newline='') as report_file:
report_writer = csv.writer(report_file, delimiter=',', quotechar='"', quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
report_writer.writerow(['project_key', 'total_loc'])
for project_key in get_project_keys():
print('Processing project', project_key)
report_writer.writerow([project_key, get_total_loc(project_key)])
To make this script work, you’ll need to install the requests in advance, the csv and sys modules are available in Python out of the box. You need to pass three arguments to the script when executed: the URL of your Bitbucket, login, and password. Here’s an example:
py script.py https://bitbucket.your-company-name.com login password
The resulting file will be saved in the same folder as the script after the execution.
How to get lines of code for each repository in the project
In case you need statistics on a particular repository you can make a single call to the Awesome Graphs’ REST API. If you need to get the total lines of code for each repository in the specified project, a simple Python script will help again. Here, the resulting CSV file will include the list of repo slugs in the specified project and their LOC totals:
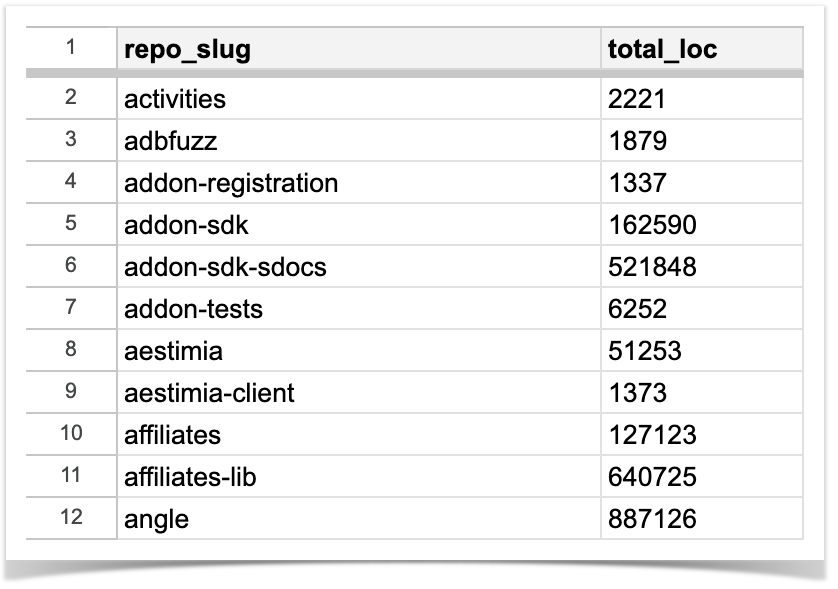
The script that will make all calculations:
import requests
import csv
import sys
bitbucket_url = sys.argv[1]
bb_api_url = bitbucket_url + '/rest/api/latest'
ag_api_url = bitbucket_url + '/rest/awesome-graphs-api/latest'
s = requests.Session()
s.auth = (sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3])
project_key = sys.argv[4]
def get_repos(project_key):
repos = list()
is_last_page = False
while not is_last_page:
request_url = bb_api_url + '/projects/' + project_key + '/repos'
response = s.get(request_url, params={'start': len(repos), 'limit': 25}).json()
for repo in response['values']:
repos.append(repo['slug'])
is_last_page = response['isLastPage']
return repos
def get_total_loc(repo_slug):
url = ag_api_url + '/projects/' + project_key + \
'/repos/' + repo_slug + '/commits/statistics'
response = s.get(url).json()
total_loc = response['linesOfCode']['added'] - response['linesOfCode']['deleted']
return total_loc
with open('total_loc_per_repo.csv', mode='a', newline='') as report_file:
report_writer = csv.writer(report_file, delimiter=',', quotechar='"', quoting=csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL)
report_writer.writerow(['repo_slug', 'total_loc'])
for repo_slug in get_repos(project_key):
print('Processing repository', repo_slug)
report_writer.writerow([repo_slug, get_total_loc(repo_slug)])
To make it work, you need to pass the URL of your Bitbucket, login, password, and project key. Here’s an example:
py script.py https://bitbucket.your-company-name.com login password PROJECTKEY
Once the execution is finished, the resulting file will be saved in the same folder as the script.
Want to learn more?
We should note that the total LOC we get in each case shows the number of lines added minus lines deleted for all branches. Due to these peculiarities, some repos may have negative LOC numbers, so it might be useful to look at the LOC for a default branch and compare it to the LOC for all branches.
If you would like to learn how to get this information with the help of Awesome Graphs for Bitbucket, write here in the comments or create a request in our Help Center, and we’ll assist you.
If you also looking to search for commits in Bitbucket, our blog post suggests three different ways to do this.